변연저에코대를 가진 동맥문맥 단락을 동반한 간혈관종
Hepatic Hemangioma with Hypoechoic Halo Accompanied by Arterioportal Shunt
Article information
Abstract
간혈관종에 동반되는 동맥문맥 단락은 종양의 유입동맥과 나란히 반대방향으로 향하는 간문맥혈류를 색도플러 초음파검사로 관찰함으로써 진단이 가능하다. 또한 종양 주변 동맥문맥 단락에 의하여 간문맥 내의 지방이 희석됨으로써 국소지방결핍 소견을 보이고 이로 인하여 혈관종 주변에 저에코성 달무리를 관찰할 수 있어서 간세포암, 종괴형성형 간내담관암 그리고 전이성 간암에서 보이는 저에코성 달무리와 감별이 필요한 질환이다. 저자는 초음파검사에서 관찰된 저에코성 달무리가 동반된 고에코성 종양을 색도플러 초음파검사, 조영증강초음파검사 및 전산화단층촬영검사를 통해 동정맥단락을 동반한 간혈관종으로 진단했던 증례를 보고하는 바이다.
Trans Abstract
Typical ultrasonographic findings of hepatic hemangioma are well demarcated, hyperechoic, homogenous mass. In case of hepatic hemangioma accompanied by arterioportal shunt, hypoechoic halo can be identified due to dilution of portal blood by nonlipid-rich arterial blood. Hypoechoic halo can also be observed in patients with malignancy such as hepatocellular carcinoma, mass forming cholangiocarcinoma and metastatic cancer. Color doppler ultrasonography can depict penetrating artery, intratumoral flow and retrograde hepatofugal portal venous flow in patient with hepatic hemangiomas accompanied by arterioportal shunt. So in patients with hepatic hemangioma with hypoechoic halo, we have to differentiate from other diseases through clinical findings, color doppler ultrasonography, contrast-enhanced ultrasonography and computed tomography. Author reports a case of hepatic hemangioma with hypoechoic halo accompanied by arterioportal shunt with the help of color doppler, contrast-enhanced ultrasonography and computed tomography.
서 론
전형적인 간혈관종은 비교적 경계가 분명한 고에코의 종괴로서 변연저에코대를 동반하지 않으나 동맥문맥 단락(arterioportal shunt)을 동반한 간혈관종에서는 종양 주변의 지방회피현상으로 인한 저에코대를 보여서 악성 종양의 달무리와 감별이 필요한데, 본고에서는 초음파검사에서 두꺼운 변연저에코대를 동반하여 악성 종양과의 감별이 필요했던 간혈관종 증례를 보고하는 바이다.
증 례
70세 남자 환자가 건강검진을 위해서 본원을 방문하였다. 과거력과 가족력에서 특이 소견이 없었고, 신체검사 결과 정상이었다. 기본 혈액검사에서 특이 소견이 없었고, 혈청검사상 A형, B형 및 C형 간염검사에서 모두 음성 반응을 보였다.
복부 초음파검사에서 담낭, 담도 및 췌장의 특이 소견은 없었다. 간의 segment 4에 1.5 × 2.5 cm 크기의 주변과 경계가 분명한 난원형의 고에코 종괴가 관찰되었고 변연에는 7 mm의 두꺼운 저에코 달무리가 동반되었다. 종괴 주변 문맥혈전은 관찰되지 않았다(Fig. 1).
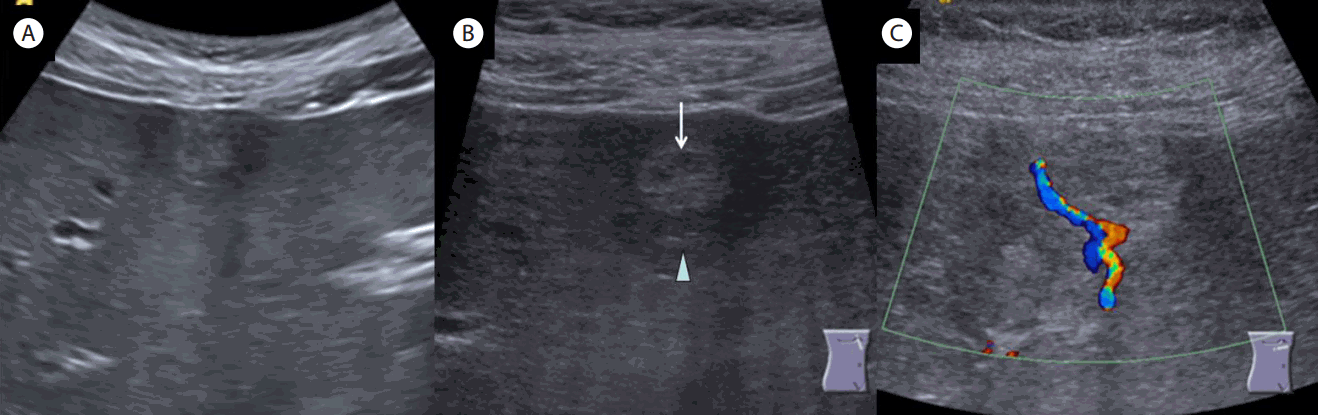
(A) Gray scale ultrasonography (4 MHz) showed about 1.5 × 2 cm (calipers not shown) sized echogenic mass with marginal thick hypoechoic halo was noted at segment 4 of the liver. (B) Gray scale ultrasonography (9 MHz) showed echogenic mass (arrow) and thick hypoechoic halo (arrowhead). (C) Color doppler ultrasonography (9 MHz) showed large feeding artery (red color) and retrograde (centrifugal, blue color) portal venous flow parallel to the feeder.
색도플러 초음파(color doppler ultrasonography)검사에서 종괴로 유입되는 유입동맥(feeding artery)과 이와 평행하게 역행성 원간성 문맥혈류(hepatofugal portal flow)가 관찰되고 있어 종양의 주변에 동맥문맥 단락이 있음을 시사하였다(Fig. 1). 이상의 초음파검사 소견으로 볼 때 간혈관종과 동반된 동맥문맥 단락을 의심할 수 있었으나 악성 종양에 의한 저에코의 달무리와 감별이 필요하여 조영 초음파와 복부 전산화단층촬영(computed tomography, CT)검사를 시행하였다.
조영초음파(contrast-enhanced ultrasonography) 검사에서 동맥기에 종괴의 변연부터 빠르게 조영되면서 종괴 주변의 저에코 부위에도 동시에 조영이 되는 양상을 보였다. 초기 문맥기에 종괴의 내부로 구심성 조영증강(centripetal fill-in) 소견이 있고 지연기까지 조영이 지속되는 양상을 보여서 동맥문맥 단락을 동반한 간혈관종 소견을 보였다(Fig. 2).
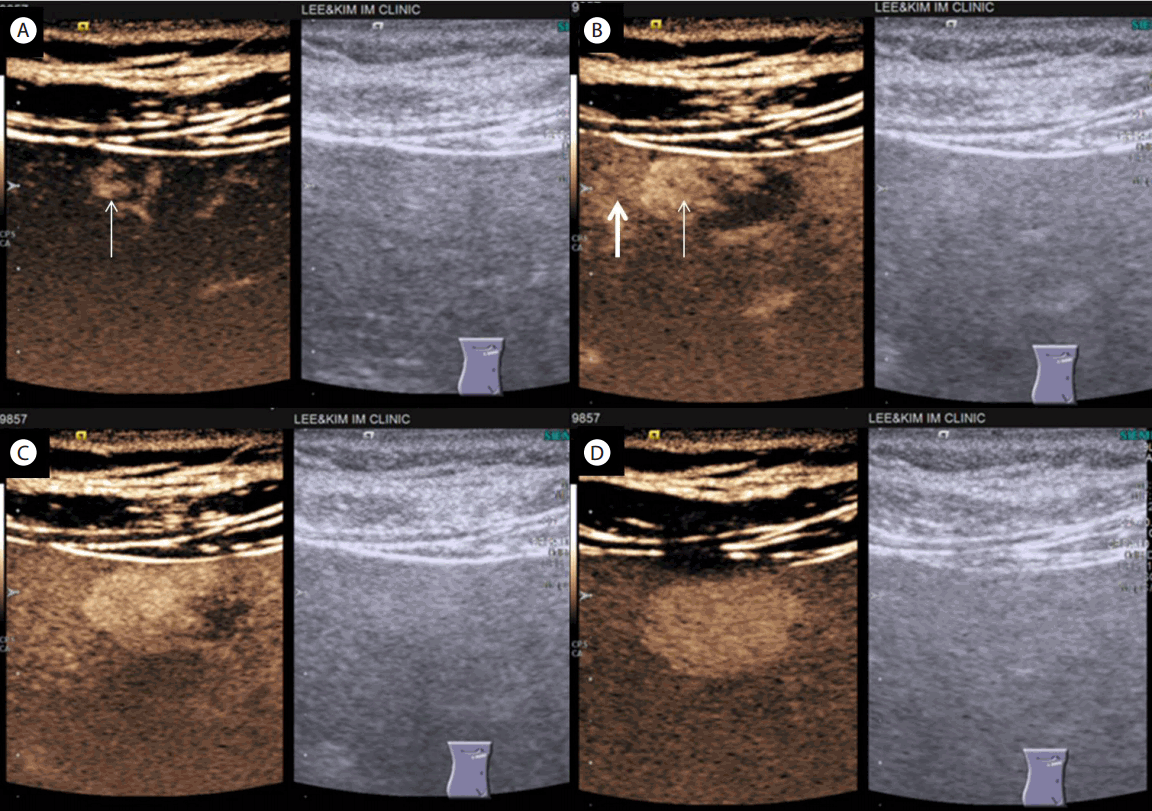
(A) CEUS performed during the arterial phase (20 seconds since contrast media injection) showed early peripheral enhancement of the mass (arrow). (B) CEUS performed during the late arterial phase (26 seconds since contrast media injection) showed rapid centripetal enhancement (thin arrow) with early peritumoral enhancement (thick arrow) which is compatible with arterioportal shunt. (C) CEUS performed during the portal phase (41 seconds since contrast media injection) showed rapid centripetal enhancement of the mass. (D) CEUS performed during the delayed phase (169 seconds since contrast media injection) showed persistent homogenous enhancement of the mass without washout of contrast agent. CEUS, contrast-enhanced ultrasonography.
CT 검사에서 종괴는 동맥기에 주변부 구형의 조영증강(peripheral globular enhancement), 문맥기에 빠른 구심성 조영증강 양상, 지연기에는 지속적인 조영 양상을 보여 간혈관종으로 진단되었다(Fig. 3). 하지만 동맥문맥 단락 시에 보이는 동맥기의 쐐기모양의 종양주변 조영증강(wedge-shaped peritumoral hyperenhancement)은 관찰되지 않았다.
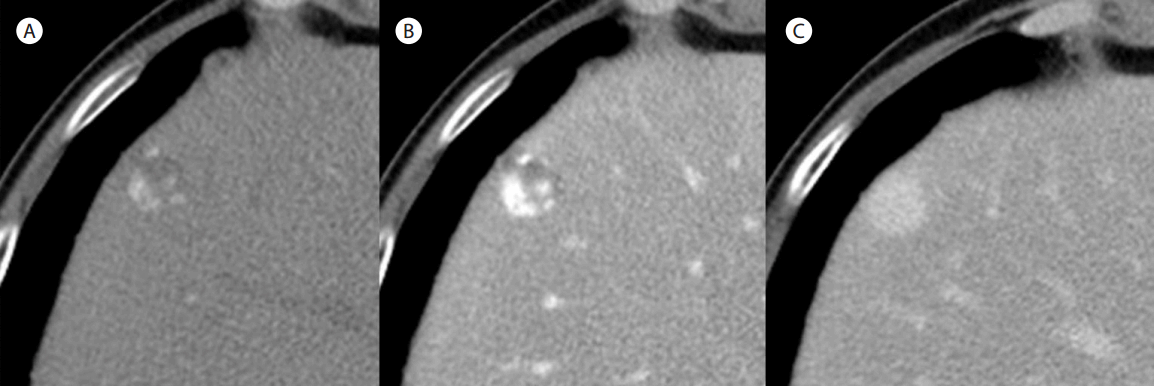
(A) CT scan performed during the arterial phase showed peripheral nodular, globular, discontinuous enhancement of the mass. (B) CT scan performed during the portal phase showed rapid centripetal fill-in. (C) CT scan performed during the delayed phase showed persistent homogenous hyperenhancement of the mass. CT, computed tomography.
이 환자는 복부 초음파, 조영증강초음파 및 CT 검사 결과 변연저에코대를 가지는 동맥문맥 단락을 동반한 간혈관종으로 진단하여 정기적인 추적검사를 하기로 하였다.
고 찰
간혈관종의 전형적인 초음파 소견은 비교적 경계가 분명한 고에코성 종괴이며, 경우에 따라서 종괴가 등에코인 경우 변연부의 고에코 병변을 동반할 수 있다[1]. 하지만 간혈관종에서 저에코성 달무리가 관찰되는 경우 간세포암, 종괴형성형 간내담관암, 전이성 간암 등의 악성 종양과의 감별이 필요하다. 간세포암에서의 저에코성 달무리는 팽창성 발육을 하는 간종괴에 의해서 주변 정상 간세포가 압박이 되어 생기는 가성피막의 형성에 의한 것으로 간세포암의 위험인자가 있는 환자에서 모자이크양상(mosaic pattern), 측방음영(lateral shadow), 문맥혈전(portal vein thrombosis)을 동반하는 종괴인 경우 감별에 도움이 되는 소견이다[2]. 종괴형성형 간내담관암에서도 저에코성 달무리를 관찰할 수 있으나 이 경우 담관확장, 간표면의 함몰 등의 소견이 동반되어 감별에 도움을 준다[3]. 전이성 간암에서도 변연 저에코대를 관찰할 수 있으며 간세포암에 비해서 두껍고 경계가 불규칙한 경우가 많으며 원발암의 병소를 확인하면 진단에 도움을 준다[4]. 반면 간혈관종 주변의 저에코성 달무리는 동맥문맥 단락과 연관되는데, 문맥에 비해서 상대적으로 지방성분이 적은 동맥혈류에 의해서 문맥혈류가 희석됨으로써 국소지방결핍이 초래되어 상대적으로 저에코성 달무리로 보인다고 한다[5]. 본 증례에서도 고에코의 간혈관종 주변에 7 mm 두께의 저에코 달무리가 동반되어서 동맥문맥 단락을 동반한 고혈류 간혈관종(high-flow hemangioma)에 의한 소견으로 볼 수 있었다.
간종괴의 초음파 진단에 있어서 색도플러 초음파검사법은 많이 이용되고 있으나 대부분의 전형적인 간혈관종의 경우 종괴 내부로의 혈류속도가 느리기 때문에 간혈관종의 진단에는 과소 평가되어 있다[6]. 하지만 동맥문맥 단락을 동반한 고혈류 간혈 관종에서는 종괴 내부로 빠른 혈류 소견을 보인다.
동맥문맥 단락을 동반한 간혈관종의 전형적인 색도플러 초음파 소견은 종괴 내부로의 큰 관통동맥(large penetrating arteries), 종괴 내의 혈류(intratumoral flow) 그리고 종괴 주변의 원간성 문맥혈류 등의 소견을 보인다고 한다[6,7]. 이러한 전형적인 색도플러 초음파검사 소견은 병변이 깊숙이 위치한 경우에는 초음파빔의 감쇠로 인하여 잘 관찰하기 어렵고 본 증례에서처럼 병변이 탐촉자에서 가까이 위치한 표재성 병변에서 잘 관찰할 수 있다. 하지만 간세포암, 국소성 결절성 과형성 및 간선종과 같은 고혈관성 간종양에서도 색도플러 초음파검사에서 종양내 혈류를 관찰할 수 있어서 감별이 필요하다. 국소성 결절성과형성과 간선종에서는 종괴 주변의 원간성 문맥혈류가 드문 반면 간세포암에서는 문맥혈전이 동반되는 경우 동맥문맥 단락에 의한 원간성 문맥혈류를 관찰할 수 있다[8]. 따라서 문맥혈전이 없는 간종괴의 색도플러 초음파검사에서 종괴 주변의 원간성 문맥혈류가 관찰된다면 동맥문맥 단락을 동반한 고혈류성 간혈관종의 가능성을 시사한다. 본 증례에서도 고에코의 종괴 내부로 유입되는 관통동맥과 이와 나란히 종괴 밖으로 유출되는 문맥혈류 소견이 있어 동맥문맥 단락을 동반함을 알 수 있었다.
간혈관종의 전형적인 조영증강초음파 소견은 동맥기에 종양의 변연부가 조영증강되기 시작하여 문맥기, 지연기에 점진적으로 중심으로 조영이 되는 양상을 보이나[9] 본 증례처럼 동맥문맥 단락이 동반되면 동맥기에 간혈관종 주변의 저에코성 달무리 부위로 조영이 됨을 관찰할 수 있다.
동맥문맥 단락이 있는 간혈관종의 복부 CT 소견은 동맥기에 주변부 구형의 조영증강, 문맥기에 빠른 구심성 조영증강 양상을, 그리고 지연기에는 지속적인 조영 양상을 보이고 특히 동맥기에서 쐐기모양의 종양 주변 조영증강이 관찰될 수 있으나[10] 본 증례에서는 관찰되지 않았다. 이는 일반적으로 조영제 주입 후 40초에 촬영하는 CT 검사의 동맥기 촬영시기에 관찰이 되지 않았다고 볼 수 있다. 이에 비해서 조영초음파에서는 조영제 주사 후 동맥기 전체를 관찰함으로써 동맥기에 동맥문맥 단락에 의한 종괴 주변의 조영증강을 잘 관찰할 수 있다.
본 증례에서처럼 간혈관종의 변연에 저에코성 달무리가 있는 경우 임상 소견, 색도플러 초음파검사, 조영증강초음파 그리고 CT 검사 등의 소견을 바탕으로 저에코성 달무리가 동반될 수 있는 타 질환의 감별이 필요하겠다.