초음파에서 전형적인 양파 껍질 징후가 관찰되는 무증상 충수 점액낭종
Asymptomatic Appendiceal Mucocele with Typical Onion Skin Sign on Ultrasound
Article information
Abstract
충수 점액낭종의 수술 전 영상의학적 진단에서 복부 초음파 검사로 세밀하게 검사하면 복부 전산화단층촬영에 못지않은 유용한 검사이며 두 가지 검사를 병행하면 진단 및 양성과 악성의 감별, 수술적 치료의 술기 선택에 큰 도움이 될 것이다. 저자는 무증상인 환자의 복부 초음파 검사에서 양파 껍질 징후를 보이는 충수 점액낭종으로 진단하여 상급병원에서 수술한 증례를 경험하였기에 보고한다.
Trans Abstract
Appendiceal mucocele is an obstructive dilatation of the appendix caused by abnormal accumulation of mucoid material. Its incidence is 0.2-0.3% of all appendectomy specimens and it does not have typical clinical features. It can mimic acute appendicitis in patients with right lower quadrant pain. Some patients have appendiceal mucocele with acute appendicitis. For this condition, 25% of cases were asymptomatic and were discovered incidentally on ultrasound examination, computed tomography, or colonoscopy due to nonspecific abdominal symptoms. Ultrasound examination or computed tomography is an important diagnostic tool for accurate preoperative diagnosis. If mucocele is treated incorrectly, pseudomyxoma peritonei may develop. The present study reports a case of a 79-year-old male with constipation. Ultrasonography showed a typical layered echogenic pattern of the appendiceal wall (onion sign or onion skin sign), which suggested appendiceal mucocele. Computed tomography showed a dilated appendix filled with low-attenuated material, indicating a pathologic diagnosis of low-grade appendiceal mucinous neoplasm.
서 론
충수 점액낭종은 충수 내강에 비정상적인 점액성 물질이 가득 차 충수가 팽창된 것을 일컫는 용어로서 절제된 충수의 0.2-0.3%에서 발견되는 아주 드문 질환이다[1,2]. 충수 점액낭종의 특징적인 증상은 없고 우하복통을 호소하는 경우엔 급성충수염과 감별이 필요하며 간혹 급성 충수염이 동반되기도 한다[3]. 환자의 약 25%는 개복술을 시행하거나 영상의학적 검사를 시행할 때 또는 대장 내시경 검사 시에 우연히 발견된다[1,2]. 충수 점액낭종은 복부 초음파 검사나 복부 전산화단층촬영으로 정확히 진단하면 비교적 합병증 없이 치료할 수 있다[4]. 저자는 79세 남자 환자가 변비를 주소로 내원하여 시행한 복부 초음파 검사에서 전형적인 양파 껍질 징후가 관찰되어 충수 점액종양으로 진단하여 상급병원에서 충수절제술로 성공적으로 치료한 증례가 있어 보고하고자 한다.
증 례
79세 남자가 변비를 주소로 내원하여 진찰상 좌하복부에 소시지 모양의 종괴가 촉지되었으며 약물 치료에도 효과가 없어 복부 초음파 검사를 시행하였다. 복부 초음파상 좌하복부의 종괴는 분변으로 확인되었고 우하복부에서 저에코의 타원형의 종괴가 발견되어(Fig. 1A) 9 MHz의 고주파 탐촉자로 자세히 검사한 결과 내부 에코가 불균일하고 얇은 벽을 가진 경계가 좋은 종괴가 있었고(Fig. 1B), 내부에 고에코와 저에코가 교대로 층을 이루는 양파 껍질 징후가 보여(Fig. 1C) 충수 점액종양으로 진단하였으며 충수벽의 석회화는 보이지 않았다. 복부 전산화단층 촬영을 시행하여 경계가 분명한 3 × 9 cm 크기의 타원형의 저밀도 종괴가 우하복부에서 보였으며 맹장의 내벽에 붙어있어 충수 점액종양 의심된다고 하였고 림프절 종대는 없다고 판독하였다(Fig. 2A and 2B). 상급병원의 대장항문외과로 전원하여 수술하였으며 육안적으로 종대된 충수가 맹장의 내측에 붙어 있어(Fig. 2C) 충수절제술을 시행하였다. 조직 검사 결과 림프절 침범 없고 절제연에도 침범이 없는 충수에 국한된 저등급 충수 점액종양으로 진단되었다.
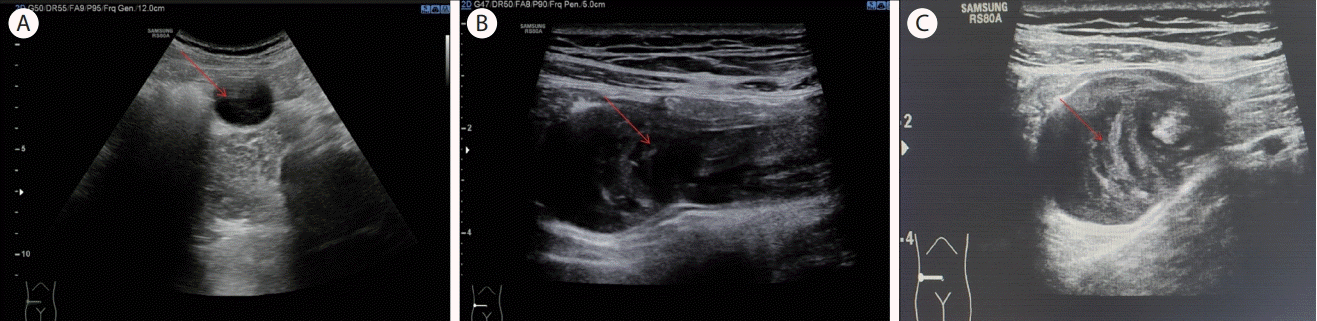
(A) Gray-scale ultrasonography (3.5 MHz) shows an oval-shaped anechoic lesion with fine internal echo (arrow) at the right lower quadrant of the abdomen. (B) High frequency (9 MHz) linear probe ultrasonography shows a tubular hypoechoic mass with various internal echogenicity (arrow). (C) High frequency (9 MHz) linear probe ultrasonography reveals a layered appearance with alternating hyperechogenicity and hypoechogenicity (onion skin sign), a typical sonographic marker of appendiceal mucocele (arrow).

(A) Computed tomography (transverse plane) shows a well-demarcated, low-density oval mass (arrow). (B) Computed tomography (coronal plane) shows a well-demarcated low-density tubular mass attached to the medial side of the cecum (arrow). No wall calcification or nodular lesion is present within the cystic lesion. Wall thickening and lymph mode enlargement also were absent. (C) The surgical field demonstrates an enlarged appendix attached to the medial side of the cecum (arrow).
고 찰
충수 점액종양은 충수 내강에 점액성 물질이 가득 차 충수가 비정상적으로 팽창된 것을 일컫는 용어로 1842년 Rokitansky가 처음 발표하였으며, 아주 드문 질환으로 전체 절제된 충수돌기의 0.2-0.3%를 차지한다[1,2]. 충수 점액종양의 특징적인 증상은 없으며 우하복부 통증을 호소하는 경우 급성 충수염과 감별이 곤란하며 간혹 급성 충수염이 동반되기도 한다[3]. 충수 점액종양의 상당수의 환자들은 증상이 없어 다른 원인으로 개복술을 하거나 대장 내시경, 복부 초음파, 복부 전산화단층촬영 등을 시행할 때 우연히 발견된다[1,2]. 이 질환은 수술 전 진단이 중요한데 치료가 지연되거나 적절히 치료를 못하면 점액이 복강 내 유출되어 복막 가성점액종이 발생하여 예후가 불량하다[1,5].
충수 점액종양은 크게 비종양성과 종양성으로 분류한다. 조직학적으로 비종양성은 저류 낭종(retension cysts), 점막 과형성(mucinous hyperplasia)으로 분류하고 종양성은 점액 낭선종(mucinou s cyst adenoma)과 점액 낭선암(mucinou s cystadenocarcinoma)으로 분류된다[6]. 2017년 미국공동암위원회 (American Joint Committee on Cancer) 8판과 2016년 국제적 복막표면종양학그룹(Peritoneal Surface Oncology Group International) 분류에 따르면, 충수 점액종양은 점액낭종(mucocele), 점액 낭선종(저등급, 고둥급), 점액 낭선암으로 나눌 수 있는데, 종양의 크기, 림프절 전이 여부, 침윤의 깊이에 따라 종양의 등급 및 병기가 결정되었다. 이런 분류는 환자의 수술적 치료방침 결정에 중요한 역할을 한다[7].
충수 점액종양의 진단에는 대장 내시경, 복부 초음파 검사, 복부 전산화단층촬영 등이 이용되고 있다. 대장 내시경에서 맹장 내강으로 융기된 형태의 입구에 충수개구부가 관찰되는 화산징후(volcano sign)를 보이면 진단이 가능하나 정상인 경우도 있다[4,8]. 복부 초음파 검사 소견은 무에코 낭성 병변으로 보이는 것부터 내부에 여러 에코가 혼재되어 보이는 것, 고에코와 저에코가 층을 이루어 양파 껍질 모양을 보이는 것(양파 껍질 징후) 등 다양한 소견을 보이며 양파 껍질 징후는 충수 점액종양의 특징적 소견이라 하겠다[6,8,9]. 양파 껍질 징후의 기전은 확실하지 않으나 두 가지의 설이 있다. 하나는 충수 내로 점액의 분비의 변동 때문이라는 설이다. 다른 하나는 충수 내강의 압력과 폐쇄의 범위의 일시적 변화 때문에 압력이 높을 때는 점액 분비의 밀도가 빽빽한 층이 생기고 상대적으로 압력이 낮은 경우는 저밀도의 점액 분비가 생긴다는 설이다[10]. 낭종벽 비후가 있거나, 낭종 내에 결절이 있거나 낭종 주위에 림프절 침범이 있으면 악성을 의심할 수 있다. 간혹 충수벽에 석회화가 보이는 경우도 있고 이로 인한 후방음영이 보이는 경우도 있다[6,8,9]. 복부 초음파 검사 시에 종괴가 발견되면 종괴의 크기, 내부 에코, 벽 비후 유무, 종괴 내부의 결절의 존재 여부, 주위 림프절 종대 유무 등을 잘 관찰해야 하겠다[6,9]. 복부 전산화단층촬영 소견은 경계가 명확한 저밀도 종괴로 보이며 충수벽의 석회화가 보일 수 있다. 낭종 주위에 림프절 전이가 있거나 낭종벽의 불규칙적인 비후, 연부 조직 비후, 낭종 내 결절이 보이면 악성을 의심할 수 있는 소견이다[5,9]. 복부 전산화단층촬영이 복부 초음파 검사보다 양성과 악성의 감별에 더 우수하다고 하나 어느 하나로서 병기 결정하는 것은 어렵다고 한다[5]. 저자의 견해로는 복부 전산화단층촬영이 림프절 전이 여부를 보는 데는 복부 초음파 검사보다 더 좋다고 생각한다. 복부 초음파 검사가 검사자에 따라 차이가 많고 비만이나 장내 가스에 영향을 받는다. 하지만 해상력이 좋은 초음파로 세밀하게 검사하면 방사선의 해가 없기 때문에 복부 초음파 검사가 복부 전산화단층촬영 못지않은 유용한 검사라고 생각한다. 이러한 수술 전 영상학적 진단은 수술적 치료의 술기 선택(충수절제술 단독, 우측 대장절제술 병행 등)에 영향을 줄 수 있다[7]. 충수 점액종양의 치료는 수술이 원칙이며 비종양성 충수 점액종양이나 충수에 국한된 저등급 점액 낭선종, 고등급 점액 낭선종, 고분화(G1) 점액선암(mucinous neoplasia)의 경우 충수절제술로 충분하다고 생각되며, 중등도(G2) 혹은 미분화(G3) 점액선암은 우측 대장절제술과 림프절 조직 검사가 필요하다. 예후는 병기와 종양의 등급에 따르며 일반적으로 비종양성 충수 점액낭종이나 저등급 점액 낭선암은 재발이 드물다[11].