서 론
담관암(cholangiocarcinoma)의 90% 이상은 조직학적으로 선암(adenocarcinoma)이며, 형태학적으로는 sclerosing type, nodular type, papillary type 3가지 종류로 나눌 수 있다. 이 중 유두상(papillary type)은 담관암 중 가장 드문 종류로 대개 총담관(common bile duct) 내 증식하는 종괴 형태로 나타나 발병 초기에 담도 폐쇄를 유발한다고 알려져 있다[1]. 폐쇄성 황달을 일으키는 다양한 양성 및 악성 췌담도 질환을 감별하기 위해서는 정확한 내시경, 영상의학, 조직학적 검사가 필수적이다. 복부 초음파는 폐쇄성 황달의 감별 진단을 위한 비침습적인 선별 도구로 널리 이용되고 있으나 총담관 원위부는 장내 가스 등으로 인해 초음파로 정확히 관찰하기 어려운 경우가 있고 추가적인 영상의학 검사 등이 필요할 수 있다. 저자는 황달을 주소로 내원한 환자에서 복부 초음파를 통해 총담관 원위부 종괴를 발견하고, 최종적으로 드문 종류의 암인 유두상담관암(papillary cholangiocarcinoma)을 진단하여 수술로 치료한 환자가 있어 이에 보고하고자 한다.
증 례
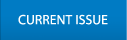
66세 여자가 4주간의 황달을 주소로 병원을 방문하였다. 내원 당시 전신 쇠약감 및 가려움, 한 달간 3 kg의 체중 감소를 호소하였다. 과거력상 고지혈증 외 특이 소견은 없었고, 술은 소주 1병(월 1회)을 마셨고, 흡연력은 없었다. 신체 진찰상 공막 황달 및 전신 황달 피부색을 보였으나 상복부 압통은 없었다. 활력징후는 혈압 105/55 mmHg, 맥박 분당 67회, 호흡 분당 20회, 체온은 36.3℃였다. 당시 백혈구 5,640/mm3, 혈색소 13.6 g/dL, 혈소판 333,000/mm3, AST/ALT 81/84 IU/L, ALP/γGTP 334/164 IU/L, 총 빌리루빈 17.7 mg/dL, amylase/lipase 57/117 IU/L, BUN/Cr 15.0/0.56, HBs Ag/Ab(-/-), HCV Ab(-), CA 19-9 43.59 U/mL였다. 복부 초음파 검사상 간내담관, 담낭, 간외담관이 확장되어 있었으며, 총담관 원위부에 1.5 × 2.1 cm 크기의 저에코 종괴(hypoechoic mass)가 발견되었다(Fig. 1).
복부 컴퓨터단층촬영상 총담관 원위부 내부에 약 2 cm 크기의 조영증강되는 종괴가 관찰되었고, 담도 확장 및 담낭 확장이 동반되었다. 자기공명영상(magnetic resonance imaging)에서 컴퓨터단층촬영과 마찬가지로 약 2 cm 크기의 총담관 원위부 종괴가 관찰되고, 지연된 조영증강(delayed enhancement) 패턴과 확산강조영상(diffusion weighted image)에서 확산 제한(diffusion restriction)이 관찰되어 간외 담관암으로 추정되었다(Fig. 2).
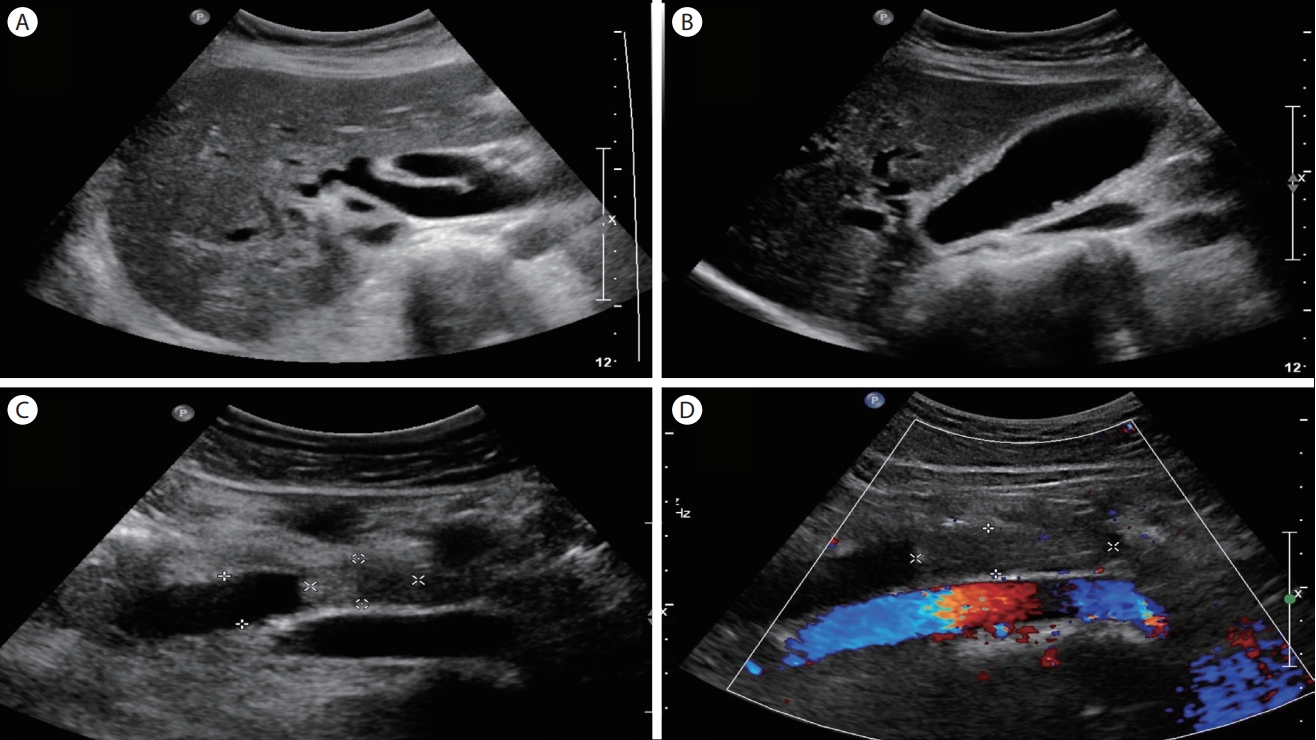
역행성 담췌관 조영술(endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography, ERCP)을 시행하였을 때, 원형의 종괴 음영이 총담관 원위부에서 관찰되고, 담도 확장이 동반되었다. 담관 내 세경초음파 촬영술(intraductal ultrasonography, IDUS) 상, 1.6 cm 크기의 유두상 종괴가 총담관 원위부에서 관찰되었고 담관 침범은 명확하지 않았다. 내시경으로 관찰 시, 처음에는 바터 팽대부가 크게 돌출되어 있었으나 점막 표면은 정상이었고, 조직 검사를 위해 내시경적 괄약근 절개술(endoscopic sphincterotomy)을 시행한 직후 종괴 일부가 십이지장 내강으로 돌출되어 올가미(snare)를 이용하여 종괴 일부를 절제하여 조직 검사를 시행하였다. 추가로 담관 플라스틱 배액관을 삽입하였다(Fig. 3).
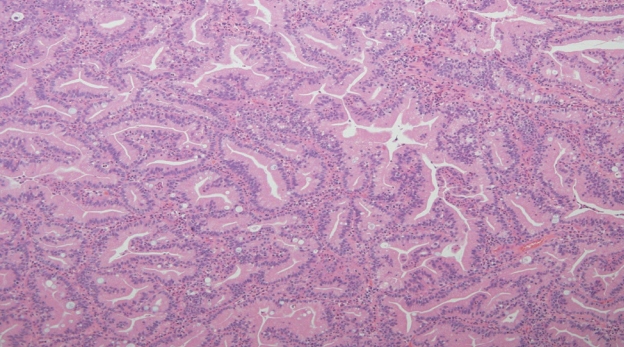
간수치는 정상화되었고, 조직 검사상 papillary adenocarcinoma로 확인되었다(Fig. 4). 양전자 방출 단층촬영(positron emission tomography-computed tomography, PET-CT)에서 원격 전이 및 주위 림프절 전이는 발견되지 않았다. 유문 보존 췌십이지장 절제술(pylorus preserving pancreatoduodenectomy)을 시행하였고 최종 병기는 T1N0M0이었다. 수술 후 특이 합병증 없이 퇴원하여 현재 외래에서 추적 관찰 중이다.
고 찰
담관암은 해부학적 위치에 따라 간내 담관암(intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma)과 간외 담관암(extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma)으로 나눌 수 있으며, 간외 담관암은 간문부 담관암(perihilar cholangiocarcinoma)과 원위부 담관암(distal extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma)으로 나뉜다. 병리학적으로 담관암의 90% 이상이 선암(adenocarcinoma)이며, 이외 편평세포암(squamous cell carcinoma) 등이 있다. 형태학적으로는 sclerosing, nodular, papillary로 분류하며, 이 중 유두상 담관암은 전체 담관암의 약 5-7% 빈도로 드물고 담관 내강 내로 증식하는 종괴 양상을 보인다[2]. 가장 흔한 임상 양상으로 무통의 황달을 호소하며 복통, 체중 감소가 동반되기도 한다. 발병 초기에 황달을 일으켜 조기에 진단되는 경우가 많고, 주변 담관 침범이나 원격 전이가 다른 형태의 담관암보다 드물어 높은 절제 가능성(resectability)과 양호한 예후를 갖는다고 보고되고 있다[1-3].
폐쇄성 황달이 있는 환자에서 복부 초음파는 손쉽게 처음 시도해 볼 수 있는 유용한 영상 검사로, 담관 폐색의 해부학적 위치를 찾고 담관 결석 혹은 담관계의 양성 및 악성 종양을 발견할 수 있다. 하지만 장내 공기 등으로 인하여 원위부 담관, 바터 팽대부, 췌장 두부 등의 위치는 초음파 검사가 제한적일 수 있으며, 이런 경우에 복부 컴퓨터단층촬영, 자기공명영상촬영 등이 추가로 필요할 수 있다. 실제로 10년 동안 폐쇄성 황달 환자 429명을 대상으로 한 연구에서 복부 초음파의 정확도는 담관 폐쇄 발견에 대해서 89%, 담관 폐쇄 위치 추정에 대해서는 94%의 민감도를 보여주었다[4].
복부 컴퓨터단층촬영은 담관암의 정확한 위치와 병기 설정, 특히 주변 혈관 침범이나 담관 침범을 평가하고 절제 가능성을 가늠하는 데 있어서 가장 널리 이용되고 있는 영상 검사다. 이중 관내 종괴(intraductal mass)에 해당하는 유두상 담관암의 경우, 조영 전 영상에서 불규칙한 경계를 가진 저감쇠(hypoattenuation) 소견과 지연된 조영증강(delayed enhancement) 패턴을 보여준다고 알려져 있다[5].
IDUS는 주로 역행성 내시경적 담도 조영술 시행 시 경유두 경로로 직접 담관 내로 세경 초음파 탐촉자를 삽입하여 병변 및 주위 구조물을 스캔할 수 있는 검사법이다. 거의 100%에 가까운 진단 정확도로 담관암의 종뱡향 범위(longitudinal extension) 탐색, 인접 장기 및 주요 혈관 침범을 식별할 수 있다고 보고되어 있다[6]. 특히 담관암 수술 범위 결정에 있어서 내시경 초음파(endoscopic ultrasonography, EUS) 검사와 비교하였을 때, 간 및 십이지장으로의 침범 부위 결정에 대해 각각 84% vs. 47%, 86% vs. 43%로 IDUS 검사가 EUS 검사보다 훨씬 정확하였다고 한다[7]. 하지만 IDUS 검사는 EUS 검사와 달리 직접 조직 검사를 할 수 없는 단점이 있다.
본 증례에서는 역행성 내시경적 담도 조영술 중 돌출된 바터 팽대부에 대해 내시경적 괄약근 절개술(endoscopic sphincterotomy)을 시행하였을 때 종괴 일부가 십이지장 내로 돌출되었다. 이는 intra-ampullary type의 바터 팽대부암에서도 볼 수 있는 소견이지만 복부 컴퓨터단층촬영, 자기공명영상촬영, IDUS, 담관 조영술 등의 결과를 종합적으로 판단하였을 때 바터 팽대부 보다는 총담관 원위부에서 기원한 종양으로 판단하였고, 최종 수술 조직 병리 검사에서도 원위부 담관암으로 진단되었다.
원위부 담관암의 근치적 절제술 후 보조적 항암 요법에 대해서는 아직 완벽히 정립되지 않았으며, 유두상 담관암의 양호한 예후를 고려하여 현재 추가 항암 치료 없이 경과 관찰 중에 있다.